Modern recruitment is undergoing one of the most significant transformations in decades. As organizations compete for skilled professionals, AI-powered tools become increasingly appealing. Yet, the rise of automated recruitment also brings complex legal questions. In Europe, for instance, data protection, equal treatment and fundamental rights shape every stage of the hiring process. Companies looking to modernize their recruitment strategies must balance innovation with compliance and responsible governance. Drawing on Finland’s example, this Katrium blog explores how modern recruitment is evolving, what legal frameworks matter the most and why a human-centered approach is still necessary.
AI in Modern Recruitment: A Case Study
To simplify the legal framework detailed below, let’s start with a fictional case study illustrating a typical modern recruitment scenario: a company implements an AI-driven applicant screening tool to handle large applicant flows. The system promises cost savings, faster processing times and more consistent recruitment decisions. The HR department is enthusiastic. Initially, applications are processed within seconds, with the AI ranking candidates based on predicted job suitability.
But within weeks, concerns arise. The model collects extensive personal data and cross-references online information that applicants never provided directly. Some candidates report receiving fully automated rejections without any human involvement. Others discover that the system scores applicants differently based on linguistic patterns correlated with nationality.
Can you spot the legal issues in the scenario detailed above? This fictional example reflects emerging real-world trends: AI is powerful, but without legal safeguards, it risks violating applicants’ privacy, undermining equal treatment and damaging employer reputation.
Modern Recruitment and the EU AI Act
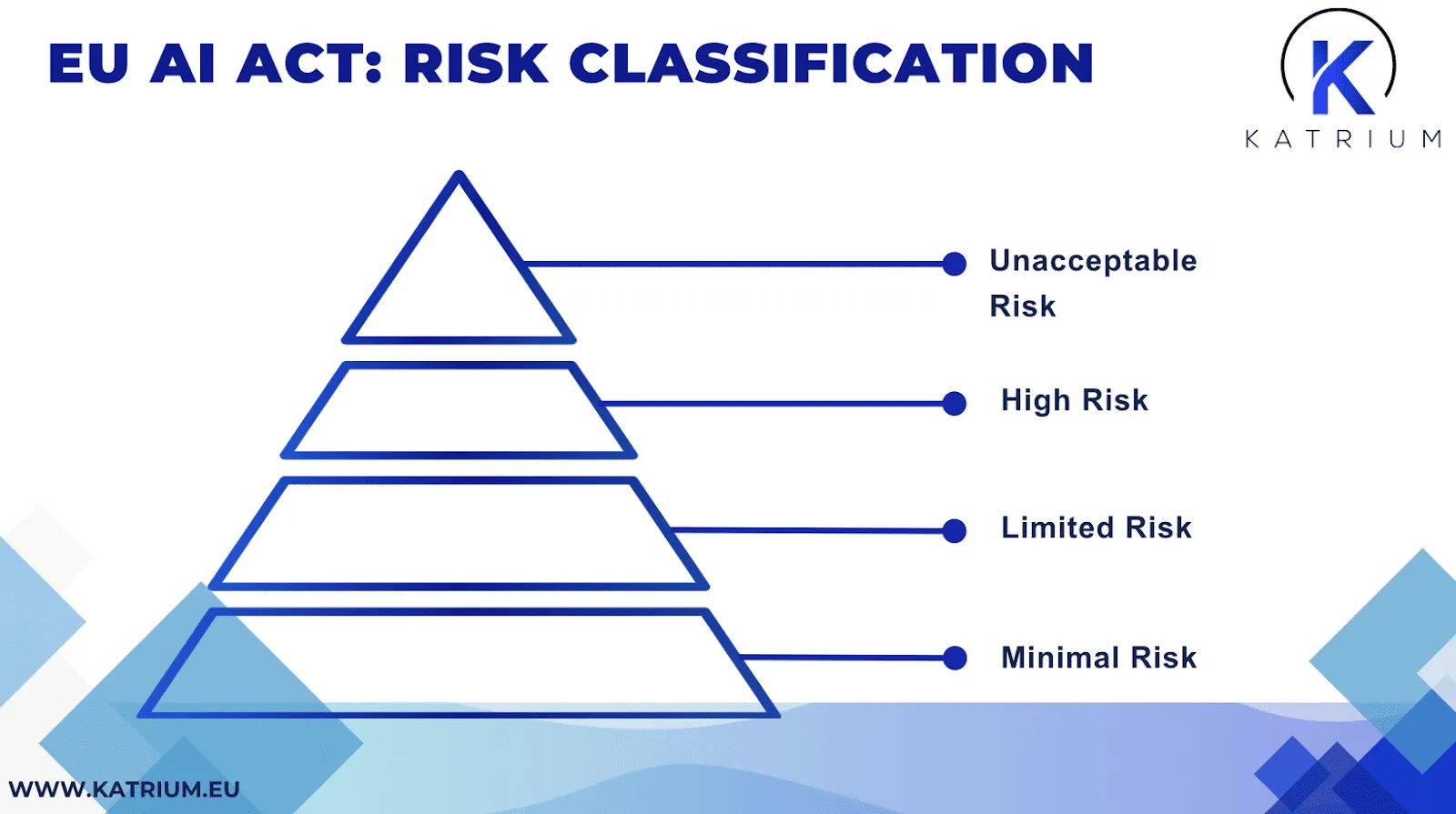
One of the most relevant frameworks applicable to modern recruitment is the EU AI Act, which entered into force in 2024. It introduces the first comprehensive regulatory framework for artificial intelligence in the European Union. The regulation is particularly important for recruitment, as AI systems used in hiring, screening or evaluating candidates are explicitly classified as high risk.
Under this high risk classification, any employer or service provider using AI for recruitment must meet a set of strict compliance obligations. These include requirements for high quality, representative data sets to reduce the risk of bias, detailed documentation of how the system operates, meaningful human oversight over automated decision making and continuous risk mitigation measures throughout the system’s lifecycle.
In practice, the AI Act requires organizations to ensure clear disclosure to candidates that AI systems are used in screening or selection. Processes should guarantee fairness, transparency and non-discrimination, while human oversight should allow persons to review, challenge or override AI decisions. There should also be strong security, audit trails and technical monitoring, as well as ongoing assessments of the AI system to detect errors, bias or discriminatory patterns.
Importantly, the AI Act applies not only to organizations established within the EU but also to companies located outside the EU, so long as their AI system’s output is used for individuals within the Union. This means that global employers using modern recruitment techniques with candidates in EU markets must comply with the regulation. Employers who fail to follow the AI Act risk significant financial penalties, reputational damage and potential legal disputes.
Data Protection as the Backbone of Modern Recruitment
Besides the AI Act, European rules surrounding data collection in recruitment are wide ranging. The cornerstone is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), supported by the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights, national constitutions and several national laws.
Under GDPR, employers may only process personal data if a clear lawful basis exists. Furthermore, applicants enjoy extensive rights, such as access, rectification, objection and data portability. Modern recruitment technologies must therefore be built with transparency, purpose limitation and data minimization in mind. For instance, one of the most important provisions is Article 22 GDPR, which restricts fully automated decision-making that produces significant effects, including rejections. Employers cannot allow AI tools to make final hiring decisions, unless specific exceptions apply and meaningful human oversight is guaranteed.
National Laws and Data Protection
Member states have also introduced additional rules. In Finland, one of Katrium’s key markets, for instance, several laws supplement GDPR, including:
- The Data Protection Act, detailing national safeguards.
- The Act on the Protection of Privacy in Working Life, which limits the information employers may collect.
- The Act on Electronic Communications Services, regulating digital data environments.
These frameworks mean that employers using modern recruitment strategies cannot collect applicant data from any external source, unless the applicant provides it themselves. AI tools scraping social media profiles or external databases would therefore breach Finnish privacy law.
Furthermore, recruitment may often involve background checks, but these are also controlled by laws such as the Security Clearance Act, the Act on Checking the Criminal Background of Persons Working with Children as well as the Occupational Health Care Act. Additionally, Finnish law requires employers to obtain specific information in certain situations. As an example, the Young Workers Act requires proof of age or school attendance, while the Aliens Act obliges employers to verify applicants’ legal right to work. Such acts affect AI-based recruiting tools further.
Equal Treatment, Non-Discrimination and Transparency
As seen above, modern recruitment should thus focus on operating within a carefully defined legal space. Even if an employer meets all data protection requirements, AI recruitment tools must also comply with non-discrimination and equal treatment rules. These stem from various legal sources, including EU freedom of movement law prohibiting nationality-based discrimination.
In Finland, relevant legal frameworks include the Non-Discrimination Act banning both direct and indirect discrimination, the Act on Equality Between Women and Men ensuring gender equality as well as the Employment Contracts Act requiring equal treatment of employees and applicants.
After all, AI systems may unintentionally discriminate if trained on biased historical data. For example, if an algorithm learns from past hiring patterns, it may favor certain demographic groups over others. Employers remain responsible for such outcomes, even when they result from automated processes rather than human action.
Human rights principles reinforce these obligations. Rights such as freedom of thought and religion, free expression, as well as the freedom to choose an occupation are not directly binding on private employers, but they influence interpretations of fairness and transparency. Ultimately, they may effectively create unwritten expectations for responsible modern recruitment.
Intellectual Property, Criminal Liability and Compensation Risks
Building or deploying AI-based modern recruitment tools involves additional legal fields. Developers and employers must consider, for instance, copyright, patents, utility model rights as well as trade secrets law. These areas regulate how data, models, training materials and system outputs may be used. Unauthorized scraping or re-use of copyrighted material may expose the company to liability.
Criminal law cannot be overlooked either. Certain data processing practices, especially those involving sensitive personal information, may lead to sanctions under national criminal codes. If applicants suffer harm due to unlawful data processing or discrimination, tort liability and compensation claims may follow. As in all regulated areas, administrative sanctions from data protection authorities represent a further risk.
Where Outsourcing Comes In
Modern recruitment requires compliance across many overlapping legal areas. For many companies, especially those expanding into new markets or hiring internationally, managing this complexity in-house is challenging. This is where outsourcing can provide significant strategic value.
Katrium, for example, supports businesses through our recruitment and HR services. Our on-demand staffing service, for instance, provides you with a temporary multilingual employee, with no need for an internal recruitment process. Additionally, our multilingual market research, outreach and communications are always handled by trained professionals who understand local legal and cultural expectations. When recruitment processes involve cross-border candidate engagement, human expertise combined with compliant data handling reduces risks. At the same time, authentic communication is maintained.
Outsourcing elements of modern recruitment, including applicant communication or data collection, therefore helps companies maintain both efficiency and legal compliance, without relying exclusively on automated systems. Let us take care of the background work while you focus on your core business!
The Future of Modern Recruitment
AI will continue playing a central role in modern recruitment, but success depends on balance. Businesses must use automation to enhance human judgment, not replace it. Transparent processes, legal compliance and an awareness of cultural and ethical issues are essential for building trust with potential candidates and maintaining a positive employer brand. As the legal landscape evolves, employers who adopt thoughtful, responsible and human-centered recruitment strategies will be best positioned to thrive.
If you’d like support in navigating multilingual candidate communication, outreach or market expansion, Katrium offers professional services built on local expertise and human connection. Modern recruitment doesn’t have to be complicated. We help ensure that your recruitment processes remain compliant and effective. Contact us now to discuss your situation further!






